Blue-Green, Rolling, and Canary: Continuous Deployments Explained
If you still rely on big-bang deployments or are ever afraid to break your production environment when you push changes, then it is seriously time to invest in building a strong CI/CD pipeline.
Pushing changes quickly and often is critical:
- It simplifies troubleshooting when deployment issues arise.
- It shortens the time between code being written, code being deployed, and the value it creates by going live.
- Not deploying continuously can have staggering financial implications.
The best way to mitigate the risks of new releases is to have a strong deployment strategy in place. Continuous deployment automates the deployment process, which lets you deliver new features and improvements to your applications faster than before.
In this blog post, we look at continuous deployment and the main implementation models you need to know: blue-green, rolling, and canary. We also explore how your application can benefit from a native CD pipeline when you deploy on a serverless platform like Koyeb.
Table of contents
- CD stands for Continuous Delivery and Continuous Deployment
- The three main Continuous Deployment Strategies: Blue-green, Rolling, and Canary
- Built-in continuous deployment on the Koyeb Serverless Platform
CD stands for Continuous Delivery and Continuous Deployment
When discussing CD, it's important to clarify if you are talking about continuous delivery or continuous deployment. The key difference between the two is how tested code is pushed into production.
- Continuous delivery: A manual choice to push the changes into production after the code has been developed, built, and tested.
- Continuous deployment: Automatic deployment of software after it has been developed, built, and tested.
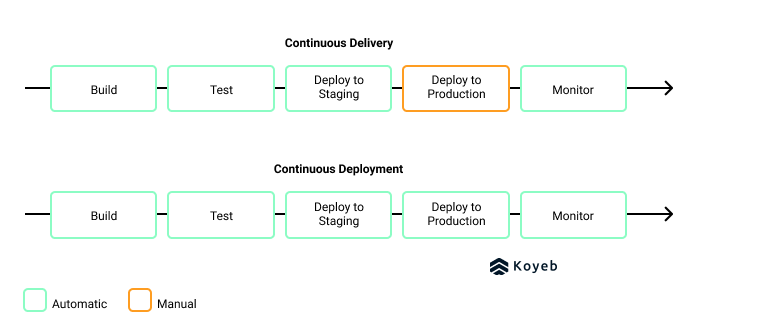
Continuous deployment requires strong testing, monitoring, and roll back capabilities
There are a few key components required to build a continuous deployment pipeline:
- Strong testing capabilities: Successfully deploying new, healthy, versions of your services and applications requires comprehensive testing capabilities. A good practice is creating the tests while implementing the change. This way you can test the changes according to the expectations and criteria planned from the start. To improve your Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment pipeline, Jenkins, CircleCI, and GitHub Actions can automatically detect new code and trigger tests each time you push to your main code repository. Once it passes these tests, your new version can be pushed to production.
- Monitoring capabilities: When you deal with production applications, you need a monitoring system in place to check that your services are up and running. Monitoring systems are also critical to ensure your app works continuously when you release a new version of your app. This practice is especially true for automated deployments. Your monitoring capabilities will enable you to monitor the health and success of your releases as well as alert you in case a service fails or becomes unhealthy.
- Rollback plan: In case your release fails and your services become unavailable, you will want to roll back to a previous and healthy version of your application. This means your deployment strategy will need backward and forwards compatibility.
Continuous deployments create a virtuous cycle
With a continuous deployment pipeline in place, you will be able to iteratively develop your application and share new releases with your users to improve their experience and add functionalities to your application faster than before.
The benefits of continuous deployment are numerous.
- By adopting a strong CI/CD pipeline, you will reduce the amount of time between writing useful code and pushing it into production.
- With smaller changes happening more often, it becomes simpler to troubleshoot and debug changes when issues arise.
- Your features gain a faster time-to-market, which gives your users a faster time-to-value.
- Moreover, your users can give you feedback sooner, meaning you can optimize and innovate your application faster.
The three main Continuous Deployment Strategies: Blue-green, Rolling, and Canary
Now that we have discussed what is continuous deployment, its components, and benefits, let's discuss the different release models you could implement to achieve continuous deployment as well as their relative advantages and trade-offs.
Once you identify a deployment strategy you want to use for your application, then you can decide how you will implement your CD pipeline. You could choose to build your own CD pipeline with the popular open source technology Spinnaker or you could opt to use the built-in CD pipeline on a cloud service provider like Koyeb.
Blue-green deployment 🔵🟢
A blue-green deployment strategy requires two identical production environments: one is known as the blue environment and the other one is the green environment.
The green environment is the live production environment, running the current version of the service while the blue environment is running a replica of the green environment with the new version of the service.
Implementation
In a blue-green deployment, tests are performed on the blue environment to ensure it is ready to handle production traffic. Once the tests passed successfully, you can promote the new version in production by reconfiguring your load balancers or proxy servers to switch the incoming traffic from the green environment to the blue environment, running the latest version of your application.
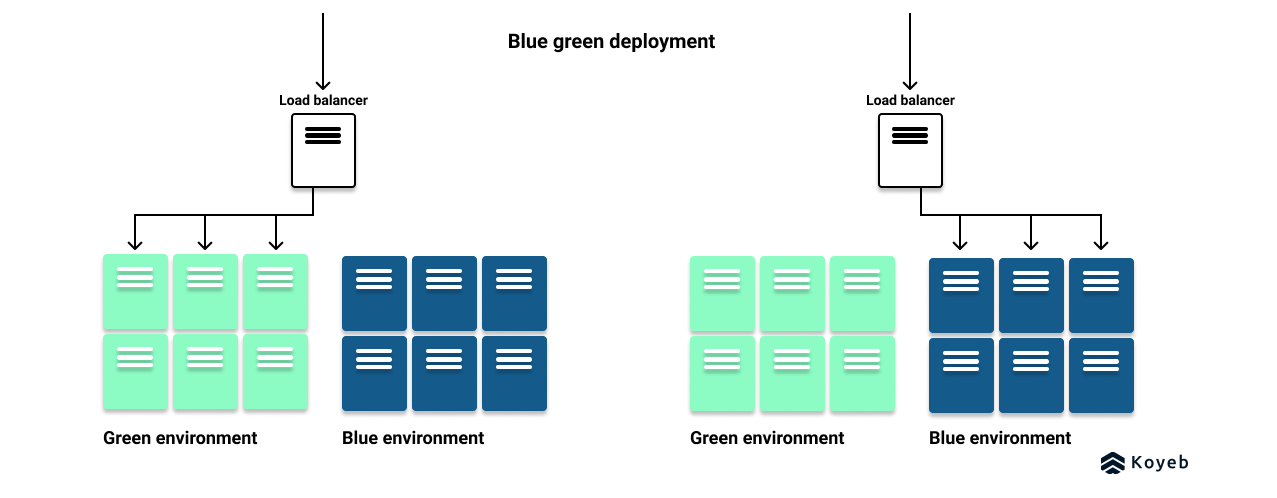
After traffic is routed to the blue environment, the green environment stops receiving new requests, but still returns responses for the in-flight requests and requests it already received. The blue environment begins processing the new requests while the health status of this environment is monitored.
If the blue environment becomes unhealthy or fails for whatever reason, then you roll back to the green environment to minimize downtime. On the other hand, if the blue environment remains healthy and available, then the new release is successfully promoted and the old green environment can be destroyed.
Blue-green deployment is the continuous deployment strategy we provide by default on Koyeb. All applications natively benefit from zero-downtime deployments.
Benefits
The advantages of blue-green deployment include:
- Eliminates downtime compared to big-bang deployments where services would go offline before the new version was launched
- Rollbacks are as simple as a click and thus lightning fast
Drawbacks
The drawbacks of blue-green deployment are:
- Doubling the infrastructure means doubling the resource cost. This cost increase can be temporary if you rely on a cloud service provider where the additional resources can be immediately destroyed after deployment.
- Keeping the two environments in sync and up-to-date can be challenging
- In case of a failure undetected by the automated testing, all requests routed to the new instances are affected.
Rolling deployment 🚌
In a rolling deployment, infrastructure instances of the previous version are slowly replaced with nodes running the new version iteratively, or in other words, in a rolling manner - hence the name. This approach is less drastic than a blue-green deployment because the new version is eased into production.
Implementation
In a rolling deployment, you will have old and new versions live at the same time until the new version completely replaces the old version. To implement a rolling deployment, you will need to run at least N + 1 instances of your application. The additional node is used to run the new version of your application.
Once the instance of the new version is released, its performance and its error rate are monitored. If the new version passes necessary health checks, then another instance is pushed into production and monitored. This process repeats iteratively until the new version is the only version up and running.
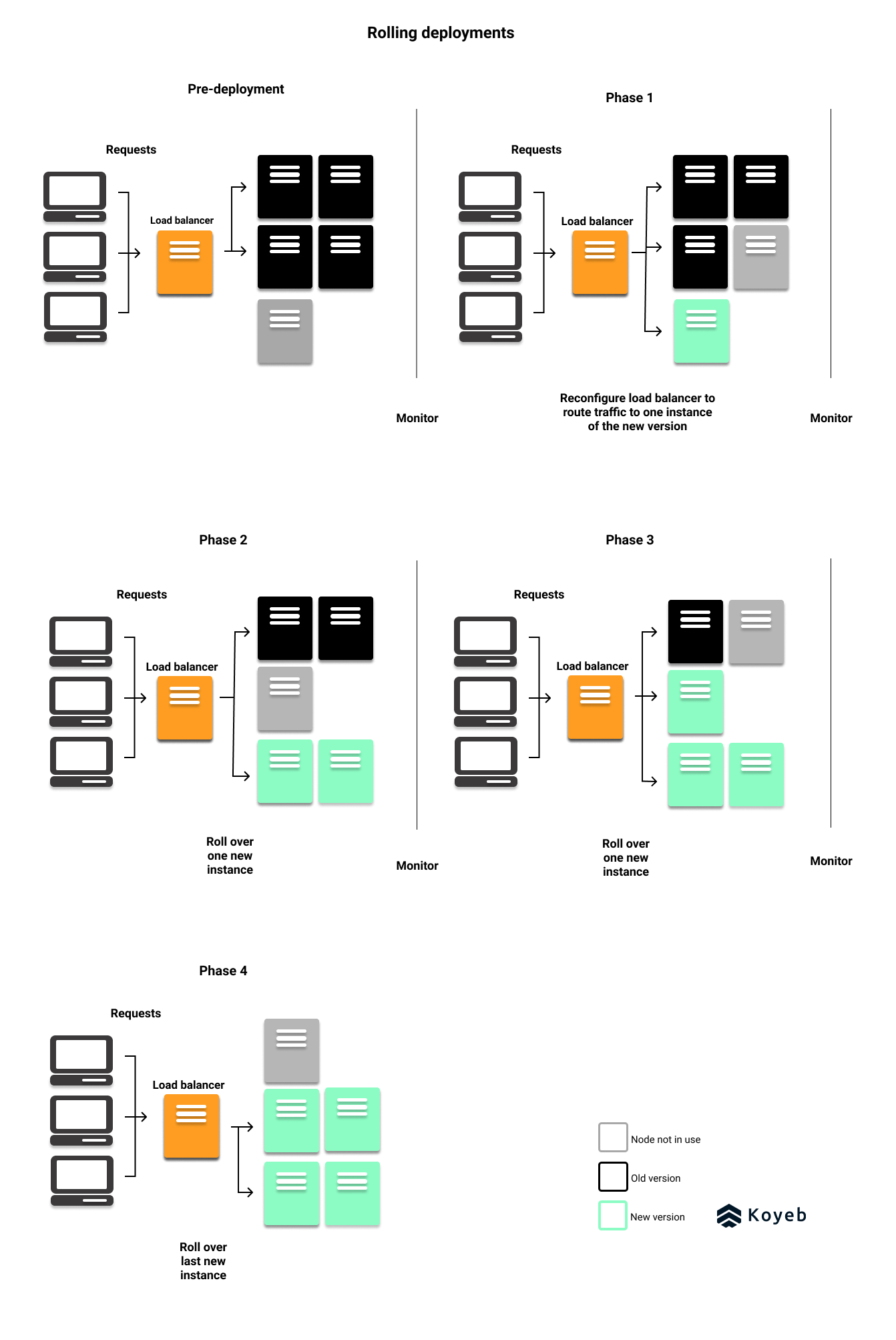
If you're a Kubernetes user, rolling updates are a standard deployment method.
Benefits
The benefits of a rolling deployment include:
- Minimal downtime as current versions stay live
- Require a minimum of one additional node (instead of an entire duplicated infrastructure like in blue-green deployments)
- In case you need to roll back, it is possible to return all traffic to the previous version
Drawbacks
The major drawback of rolling deployments:
- Depending on the number of instances your application is running, you could see a significant latency between the moment you start deploying the new version and the moment it is all live.
- If a failure occurs in the middle of the deployment process, rolling back can be really time-consuming.
Canary deployment 🦜
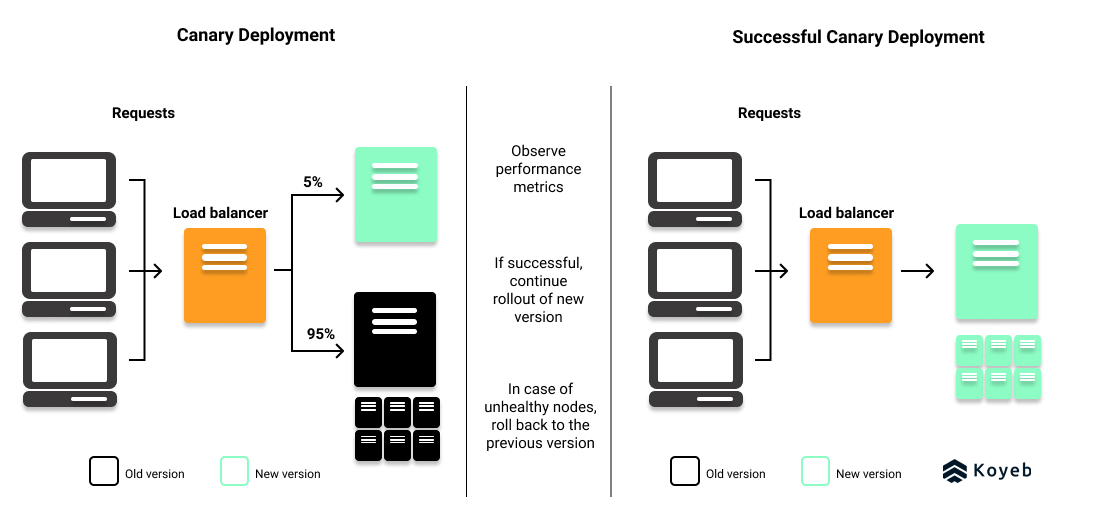
A canary deployment is an excellent deployment strategy for testing performance or technology issues. In a canary deployment, the new version is released to a small number of users by deploying the changes to a subset of servers.
Canary deployments should not be confused with A/B testing, which is for testing user experience and engagement across potential new versions.
Not so fun fact, the term refers to the history of coal miners releasing a canary into a new mine to detect odorless toxic gas before entering the mine to work.
Implementation
To implement a canary deployment, you will first need to determine the following:
- The size (1%, 5%, 10%) of the test group
- Who will be in the test group: volunteer beta users or random users
- The implementation method: You can implement a canary deployment one of two ways:
- Reconfigure the load-balancer, API Gateway, or Service Proxy that sits in front of your servers
- Use a feature flag
Once your canary deployment is released, you will then monitor the test audience's user experiences. Typical metrics people study during a canary release are latency issues, internal error counts, and excessive memory or CPU use.
If these performance metrics are satisfactory, the new version continues to roll out gradually and be monitored until the release is complete, like in a rolling deployment. However, in the case of an issue, you can roll back to the previous and healthy version of your application.
Service Proxies and API Gateways like Kong and Envoy can be used to implement canary deployments.
Benefits
The benefits of canary deployments:
- You can test the new version with real users
- Identify bugs or performance issues before releasing to a wider audience
- In case of failure, only a small number of users is affected
- Minimal infrastructure requirement especially when you use a feature flag
- Rollback is simple and quick
Drawbacks
The drawbacks of canary deployments include:
- Technical challenge to route only some users to the new version. Feature flags are the more cost-effective method.
- If you opt for feature flags, you will need a housekeeping strategy because keeping track of them at scale can introduce complexity to the codebase.
- Require advanced observability capabilities, metrics and analysis to validate new releases.
A/B Testing 🆎 should not be confused with Continuous Delivery
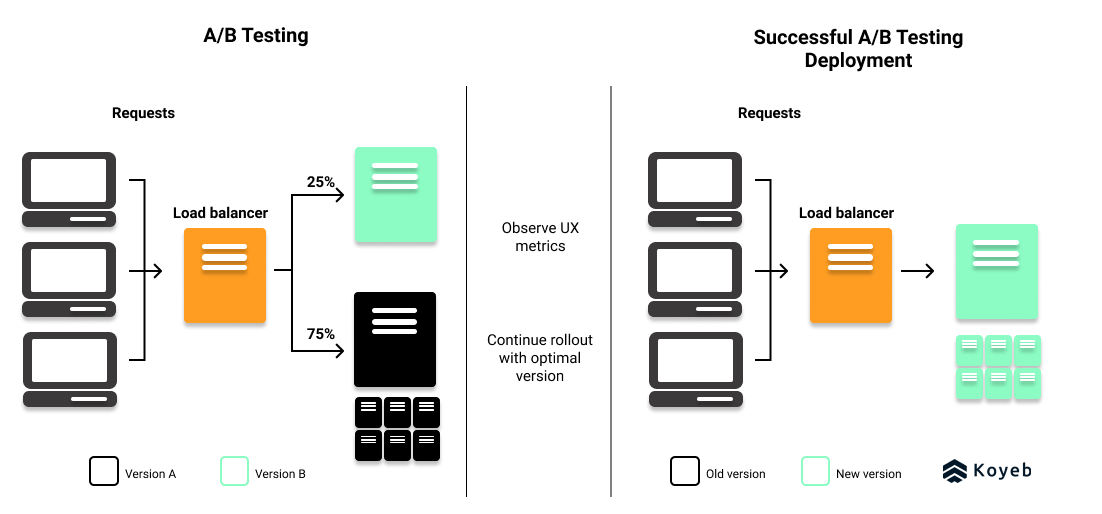
While not a deployment strategy, A/B testing resembles canary deployments except that it tests new versions along criteria for user experience rather than infrastructure performance.
With A/B testing, different versions of the same service run in production to identify the best version along user experience and engagement criteria.
Implementation
Like canary deployments, A/B deployments can be achieved with the use of a feature flag or by reconfiguring the load-balancer to route a select number of traffic to a production environment running the new version.
Strong observability capabilities are needed to collect and analyze data in order to determine if the new release can be entirely rolled out to production. In case of failure, you can return traffic to the previous version of the application.
Benefits
The advantages to A/B testing deployments:
- Test ideas in production and then pushing forward with the optimal version for your target audience.
- Small test audience means minimal downtime and performance issues experienced by users
- A feature flag is a cost-effective method to conduct an A/B test deployment
Drawbacks
There are a few drawbacks to A/B deployments:
- Require reliable and sophisticated observability, data collection and analysis capabilities.
- Extra infrastructure cost for creating a test production environment, could be as small as one node though.
Built-in continuous deployment on the Koyeb Serverless Platform 🥳🚀
There are a number of strategies you can use to continuously deploy your applications. Your uptime requirements, resource capacity, and deployment goals will determine which method is best for your use case.
In any case, building a continuous deployment pipeline requires a significant time and resource investment, and so does performing its on-going maintenance.
The great news is that this infrastructure is included out-of-the-box and from the get-go with the Koyeb Serverless Platform! This means you get all of the benefits of a CD pipeline without any of the headaches.
Each time you perform a git push to your repository, you trigger a new build and deployment for your application on Koyeb. Your changes then go live as soon as the automatic deployment passes all of Koyeb's necessary health checks. In case of deployment failure, Koyeb keeps your latest working deployment active so your application is always up and running.
Your deployment strategy influences your time-to-market. Create and share value with your users faster by opting for a continuous deployment on Koyeb. Try it for free today and make sure to join us on our community platform to stay up-to-date with our latest news.